(1) Understand the variable frequency load type . The correct selection of the inverter is very critical for the normal operation of the control system. When selecting an inverter, you must fully understand the characteristics of the load driven by the inverter. In practice, people often divide production machinery into three types: constant torque load, constant power load and fan and water pump load.
(01) Constant torque load The load torque TL has nothing to do with the speed n. TL always remains constant or basically constant at any speed. For example, friction loads such as conveyor belts, mixers, and extruders, as well as potential energy loads such as cranes and hoists, are all constant torque loads. When the frequency converter drives a load with constant torque, the torque at low speed must be large enough and it must have sufficient overload capacity . If stable operation at low speed is required, the heat dissipation capacity of the standard asynchronous motor should be considered to avoid excessive temperature rise of the motor. (02) Constant power load The torque required by machine tool spindles, rolling mills, paper machines, and coilers and decoilers in plastic film production lines is generally inversely proportional to the rotational speed. This is the so-called constant power load. The constant power property of the load should be within a certain range of speed changes. When the speed is very low, due to the limitation of mechanical strength, TL cannot increase infinitely and transform into constant torque properties at low speed. If the constant torque and constant power speed regulation range of the motor is consistent with the constant torque and constant power range of the load, that is the so-called “matching” situation, the capacity of the motor and the capacity of the inverter are both minimum. 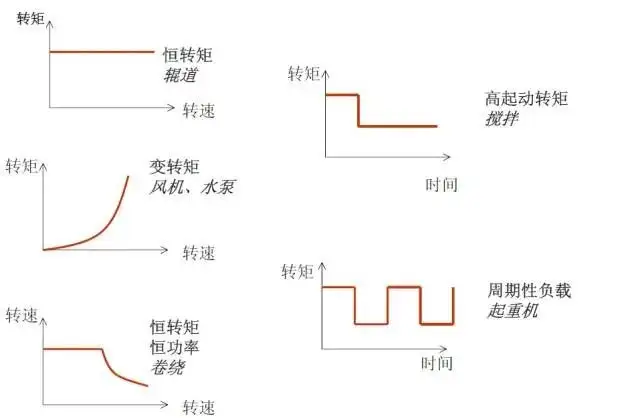
(03) Fans and pumps are loaded in various fans, water pumps, and oil pumps. As the impeller rotates, the resistance generated by the air or liquid within a certain speed range is roughly proportional to the 2nd power of the speed n. As the rotational speed decreases, the torque decreases according to the square of the rotational speed. The power required for such a load is proportional to the third power of the speed. When the required air volume and flow rate decrease, the frequency converter can be used to adjust the air volume and flow rate through speed regulation, which can greatly save electric energy. Since the power required at high speed increases too quickly with the speed and is proportional to the cube of the speed, fans and pumps should generally not be operated beyond the industrial frequency. (2) Familiar with the frequency conversion selection principles (01) Combined with the overall framework of the project, starting from the process characteristics and electrical control, the load type, usage environment, communication architecture and interface type must be considered, such as serial port, DP or PN communication interface. (02) Select the frequency converter according to the load characteristics. If the load is a constant torque load, you can choose the Siemens G120 frequency converter. If the load is a fan or pump load, you can choose the Siemens G120XA frequency converter. (03) When selecting the inverter, the actual motor currentThe value is used as the basis for selecting the inverter, and the rated power of the motor can only be used as a reference. In addition, it should be fully considered that the output of the frequency converter contains high-order harmonics, which will cause the motor’s power factor and efficiency to deteriorate. Therefore, compared with using a frequency converter to supply power to a motor compared with using a power frequency grid, the current of the motor increases by 10% and the temperature rise increases by about 20%. Therefore, when selecting the motor and frequency converter, this situation should be taken into consideration and an appropriate margin should be left to prevent the temperature from rising too high and affecting the service life of the motor. (04) When the inverter wants to run with a long cable , measures should be taken to suppress the impact of the long cable on the ground coupling capacitance to avoid insufficient output of the inverter. Therefore, the inverter should amplify one gear or install an output at the output end of the inverter. Reactor. (05) For some special applications, such as high ambient temperature , high switching frequency (especially when using in applications with high noise restrictions such as building automation), high altitude, etc., this will cause the inverter to To reduce the capacity, the inverter needs to be enlarged by one gear.
(07) For some special applications, such as high ambient temperature, high switching frequency, high altitude, etc., this will cause derating of the frequency converter, and the frequency converter needs to be enlarged by one gear.
(08) When using a frequency converter to control a high-speed motor, due to the small reactance of the high-speed motor, high-order harmonics also increase the output current value. Therefore, when selecting an inverter for a high-speed motor, it should be slightly larger than an inverter for an ordinary motor.
(09) When the frequency converter is used in a pole-changing motor, sufficient attention should be paid to selecting the capacity of the frequency converter so that its maximum rated current is below the rated output current of the frequency converter. In addition, when converting the pole number during operation, the motor should be stopped first, otherwise it will cause the motor to idle, and in severe cases, the inverter will be damaged.
(10) When driving an explosion-proof motor, the frequency converter does not have an explosion-proof structure, and the frequency converter should be installed outside of hazardous locations.
(11) When using a frequency converter to drive a gear reduction motor, the range of use is restricted by the lubrication method of the gear rotating part. When lubricating oil, there is no limit in the low speed range; in the high speed range exceeding the rated speed, there may be a risk of running out of lubricating oil. Therefore, do not exceed the maximum allowable speed.
(12) When the frequency converter drives a wound rotor asynchronous motor, most of the existing motors are used. Compared with ordinary squirrel cage motors, the impedance of the windings of wound motors is small. Therefore, overcurrent tripping due to ripple current is prone to occur, so an inverter with a slightly larger than usual capacity should be selected. Generally, winding motors are mostly used in situations where the flywheel torque GD2 is large, so more attention should be paid when setting the acceleration and deceleration time.
(13) When the frequency converter drives a synchronous motor, compared with the industrial frequency power supply , the output capacity is reduced by 10% to 20%. The continuous output current of the frequency converter is greater than the product of the rated current of the synchronous motor and the per unit value of the synchronous pull-in current.
(14) For loads with large torque fluctuations such as compressors and vibrators and peak loads such as hydraulic pumps, if the inverter is selected according to the rated current or power value of the motor, overcurrent may occur due to the peak current. protection action phenomenon. Therefore, you should understand the power frequency operation conditions and choose an inverter with a rated output current larger than its maximum current. When a frequency converter drives a submersible pump motor, because the rated current of the submersible pump motor is larger than that of a normal motor, when selecting a frequency converter, its rated current should be greater than that of the submersible pump motor.
(15) When the frequency converter controls the Roots blower, due to its large starting current, when selecting the frequency converter, you must pay attention to whether the capacity of the frequency converter is large enough.
(16) When selecting an inverter, be sure to pay attention to whether its protection level matches the on-site conditions. Otherwise, dust and water vapor on site will affect the long-term operation of the inverter.
(17) Single-phase motors are not suitable for inverter drive.
(18) When the motor load is very light, even if the motor load current is within the rated current of the inverter, an inverter with a much smaller capacity than the motor cannot be used. This is because the reactance of the motor varies with the motor capacity. Even if the motor load is the same, the larger the motor capacity, the greater the pulsating current value, which may exceed the current allowable value of the inverter. (19) If the power supply of the inverter is a self-prepared power supply, it is best to add an incoming line reactor.







